Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
豊田 実*; 解良 恭一*; 大島 康宏; 石岡 典子; 紫野 正人*; 坂倉 浩一*; 高安 幸弘*; 高橋 克昌*; 富永 英之*; 織内 昇*; et al.
British Journal of Cancer, 110(10), p.2506 - 2513, 2014/05
被引用回数:106 パーセンタイル:95.25(Oncology)Amino-acid transporters are necessary for the tumor cell growth and survival, and play a crucial role in the development of cancer. But, it remains unclear about the prognostic significance of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1), System ASC amino acid transporter 2 (ASCT2) and xCT expression in patients with tongue cancer. We conducted the clinicopathological study to investigate the protein expression of these amino acid transporters in tongue cancer. Eighty-five patients with surgically resected tongue cancer were evaluated. Tumor sections were stained by immunohistochemistry for LAT1, ASCT2, xCT, CD98, Ki-67, CD34 and p53. The expression of LAT1 and ASCT2 was significantly associated with disease staging, lymph node metastasis, lymphatic permeation, vascular invasion, CD98 expression and cell proliferation (Ki-67). xCT expression indicated a significant association with advanced stage and tumor factor, correlated with CD98. By univariate analysis, both LAT1 and ASCT2 had a significant relationship with prognosis. Multivariate analysis confirmed that LAT1 were independent prognostic factors for predicting poor prognosis. These results suggest that LAT1 and ASCT2 can serve as a significant prognostic factor for predicting worse outcome after surgical treatment and may play an important role in the development and pathogenesis for tongue cancer.
 -methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancer
-methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancer鈴木 茂正*; 解良 恭一*; 大島 康宏; 石岡 典子; 宗田 真*; 横堀 武彦*; 宮崎 達也*; 織内 昇*; 富永 英之*; 金井 好克*; et al.
British Journal of Cancer, 110(8), p.1985 - 1991, 2014/04
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:60.2(Oncology)Fluorine-18- -methyltyrosine (FAMT) as an amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography (PET) is useful for detecting human neoplasms. FAMT is accumulated in tumor cells solely via L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1). This study was conducted to investigate the biological significance of FAMT uptake in patients with esophageal cancer. From April 2008 to December 2011, 42 patients with esophageal cancer underwent both FAMT PET and FDG PET before surgical treatment. The immunohistochemical analysis of LAT1, CD98, Ki-67, CD34, p53, p-Akt and p-mTOR was performed on the primary lesions.
-methyltyrosine (FAMT) as an amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography (PET) is useful for detecting human neoplasms. FAMT is accumulated in tumor cells solely via L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1). This study was conducted to investigate the biological significance of FAMT uptake in patients with esophageal cancer. From April 2008 to December 2011, 42 patients with esophageal cancer underwent both FAMT PET and FDG PET before surgical treatment. The immunohistochemical analysis of LAT1, CD98, Ki-67, CD34, p53, p-Akt and p-mTOR was performed on the primary lesions. 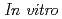 experiments were performed to examine the mechanism of FAMT uptake using LAT1 inhibitor, 2-aminobicyclo-(2,2,1)-heptane-2-carboxylic acid (BCH). High uptake of FAMT was significantly associated with advanced stage, lymph node metastasis and the expression of LAT1, CD98, Ki-67 and CD34. LAT1 expression yielded a statistically significant correlation with CD98 expression, cell proliferation, angiogenesis and glucose metabolism.
experiments were performed to examine the mechanism of FAMT uptake using LAT1 inhibitor, 2-aminobicyclo-(2,2,1)-heptane-2-carboxylic acid (BCH). High uptake of FAMT was significantly associated with advanced stage, lymph node metastasis and the expression of LAT1, CD98, Ki-67 and CD34. LAT1 expression yielded a statistically significant correlation with CD98 expression, cell proliferation, angiogenesis and glucose metabolism. 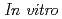 experiments revealed that FAMT was specifically transported by LAT1. The uptake of FAMT within tumor cells is determined by the LAT1 expression and correlated with cell proliferation and angiogenesis in esophageal cancer. The present experiments also confirmed the presence of LAT1 as an underlying mechanism of FAMT accumulation.
experiments revealed that FAMT was specifically transported by LAT1. The uptake of FAMT within tumor cells is determined by the LAT1 expression and correlated with cell proliferation and angiogenesis in esophageal cancer. The present experiments also confirmed the presence of LAT1 as an underlying mechanism of FAMT accumulation.